In today's interconnected environment, international product manufacturing has become a critical component for shaping successful businesses. As companies grow into new markets, there is a growing recognition the advantages of participating in international markets for design and production. This approach not only enhances creativity and innovation but also offers varied viewpoints which can result in improved product results.
A primary advantage of global manufacturing practices comes from the capacity to access specialized skills and resources often not found domestically. By collaborating with manufacturers worldwide, companies have the ability to use local expertise, cut expenses, allowing them to provide superior quality goods to consumers. Moreover, implementing a global manufacturing strategy enables companies to manage risks by diversifying supply chains, ensuring increased resilience against disruptions that may arise geopolitical issues, natural events, or other unforeseen challenges.
Understanding Worldwide Production Threats
Worldwide manufacturing offers numerous benefits, but it is not without its obstacles. Companies can face a variety of hazards that can jeopardize their manufacturing operations, such as political instability, economic instability, and regulatory changes. These elements can disrupt supply chains, raise expenses, and create ambiguity in shipping timing, ultimately affecting the general effectiveness of manufacturing operations. It is essential for companies to be aware of these risks as they expand into international territories.
An additional significant risk is the inconsistency in standard standards across different regions. Manufacturers may encounter differing rules, manufacturing methods, and quality control processes based on the place. This inconsistency can lead to products that do not meet the expected standards, resulting in potential recalls, damage to corporate reputation, or legal consequences. Businesses must prioritize establishing strict standard assurance measures to reduce these risks effectively.
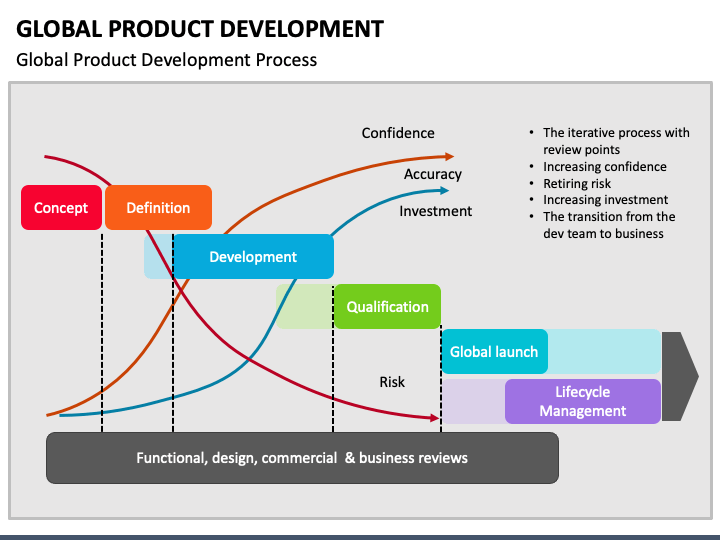
Cultural diversity also add to the difficulty of international manufacturing. Teams working across varied cultural contexts may face language barriers and conflicts, impacting collaboration and productivity. Firms can counter these challenges by fostering a environment of inclusion and ongoing training, ensuring that all team members comprehend each other's perspectives and work collaboratively towards common goals. Identifying and addressing these threats is essential for a effective international manufacturing strategy.
Approaches for Managing Risks
To efficiently mitigate risks linked to global product manufacturing, companies should adopt a multi-faceted approach focused on supply chain diversification. By sourcing materials and components from various suppliers across different geographic regions, businesses can lessen their reliance on a single source and minimize the impact of disruptions. This approach not only enhances resilience against environmental catastrophes or political instability but also encourages price competition and drives creativity among suppliers.
Another essential strategy is to establish comprehensive quality control measures at all stages of the manufacturing process. By setting rigorous standards and conducting regular inspections both in-house and on-site with suppliers, companies can verify that products meet quality expectations and regulatory requirements. This forward-thinking approach helps detect potential flaws early, avoiding costly returns or reputational damage that may arise from poor product performance.
Lastly, utilizing advanced technology and data analytics can greatly improve risk management in international manufacturing. manufacturers outside of china can use real-time data to track supply chain dynamics, track inventory levels, and foresee potential interruptions. By integrating predictive analytics, organizations can make data-driven decisions that enhance operational efficiency and flexibility. This technology-driven approach not only helps in addressing existing issues but also positions companies to take advantage of emerging opportunities in the global market.
Case Studies in Worldwide Manufacturing
One prominent case of effective global product manufacturing is Apple Inc.. The company efficiently utilizes a large, integrated supply chain that spans multiple countries. Research and development mainly occur in the U.S., while manufacturing is outsourced to countries such as China. This strategy enables Apple to reduce production costs while benefiting from a talented labor force and rapid production capabilities. By combining design innovation with affordable manufacturing, Apple has sustained its status as a market leader in technology.
Another important case is Toyota's production system, which utilizes global manufacturing methods to enhance efficiency and quality. Toyota runs production facilities in multiple countries, allowing for localized manufacturing while still maintaining its core principles of efficient manufacturing. This approach not only reduces transportation costs but also enhances responsiveness to market demands. By using cross-border collaboration, Toyota is capable to mitigate risks associated with supply chain interruptions and ensure consistent product quality.
A final example can be seen in H&M's global sourcing strategy. The fashion retailer procures materials and manufactures products from a diverse range of suppliers worldwide. By spreading its manufacturing across multiple countries, H&M ensures adaptability and robustness in its operations. This approach allows the company to adapt quickly to changing fashion trends while optimizing costs and upholding responsible production standards. H&M’s international manufacturing practices illustrate the capability for companies to enhance both their competitive edge and sustainability through thoughtful design and distribution strategies.
